BT(1) - B+树(Vec)
在前一篇的文章里介绍了 B 树,这里介绍它的变种 B+ 树的基本实现。
如果说之前好不容易把观念从二叉搜索树转换到了 B 树,那么从现在开始,从 B 树到 B+ 树又需要有一个很大的观念转变。不过请放心,本文讲得是依靠 Vec 实现的 B+ 树,后面还会介绍用 TreeMap 实现的 B+ 树,那时又需要一个很大的观念转变。
整个 B 树系列计划了四篇文章,即使层层铺叠,每篇间的学习曲线都很陡峭,可谓是一山四绝弯!
概念基础
B+ 树区别于普通 B 树的主要特点是中间节点有键无值1 ,而在最底层的叶子上存储数据。另外叶子节点存储有 next 指针,指向它的后继节点,为得是高效的范围查询。
由于更好的缓存适应性,B+ 树的基础操作 查/增/删 都明显快于普通 B 树,完全可以当做普通 B 树的上位替代。
观念挑战
虽然看起来只是一个小小的改变,但又一次颠覆了习惯的概念。
- 从二叉搜索树到 B 树,我们一直习惯的是键就是键值的代名词,但正如前面节点不再是键的代名词,这里键与值的关系也分开了;
- 进一步考虑,这就出现了叶子上必然存在一个键,而中间节点里可能还存在一个重复的键;
- 也就是说父节点的键与子节点键的大小关系也不同了,不仅是大于或者小于,还有可能是相等的关系
因此这里还要明确一下:B+ 树父节点的键可能与子节点的最小键相等,这符合左闭右开的惯例。
索引的重要性质
不是叶子节点上的每一个键值都在内部节点上有一个键,在内部节点的键有两种情况:
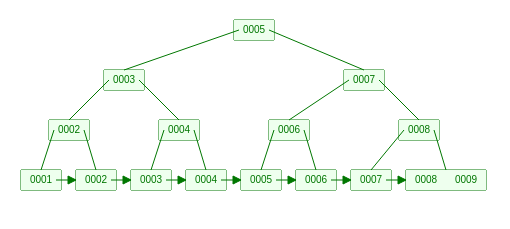
- 每个根的叶子节点,除了第一个以外,每个叶子的最小键,都在这个这个根上有对应的键,就是左键2;
- 第一个叶子节点除了最小的根以外,在根或者根的祖先上也有对应的键
也就是说,所有中间节点的键由且仅由除了第一个节点以外的每个叶子节点的最小键组成
在我做调查的过程中发现这个索引的性质在有的实现里并没有被尊重,这不会直接影响功能的实现,却破坏了 B+ 树的性质,引入了潜在的 Bug :删除会导致中间节点存在废弃的键。
重平衡
过程与 B 树一致,只是分裂节点时由弹出中间的键改为克隆中间的键,合并节点的时候只删除父节点对应键而不是并入节点,因此这里就不再赘述。
实现->数据结构
树
impl_tree!(
/// B+ Trees
///
BPT {}
);
节点包装
impl_node!();
内部节点
B+ 树叶子节点和内部节点的字段区别还是很大的,是否沿用之前的同构的设计是个值得思考的问题。
我们比较这两种设计的 drawback:
如果采用同构:
- 会有冗余字段,每个字段都占了至少是指针宽度的空间;
- 节点看起来有些杂乱,严重降低代码可读性
如果采用异构:
- 由于使用了枚举,导致之前积累的宏没法儿使用,需要重写一套,另外还要编写配套的内部节点的属性访问代码
看起来没有哪一个是写起来又好又快的,但是我们再仔细考虑发现:
- 同构的设计还是需要一个单独字段来内省地判断自己是叶子节点还是中间节点,它和异构的枚举实现的区别本质上只是一个是手搓的、特化的,一个是系统的、泛化的;
- 编程也有一个不可能三角:

一般地,条件允许下,是牺牲部分代码简洁性,来保障另外的两个目标。
因此这里我还是采用了异构的设计:
enum Node_<K, V> {
Internal {
keys: Vec<K>,
children: Vec<Node<K, V>>,
paren: WeakNode<K, V>,
},
Leaf {
entries: Vec<KVEntry<K, V>>,
/// Successor (Leaf)
succ: WeakNode<K, V>,
paren: WeakNode<K, V>,
},
}
use Node_::*;
内部节点的属性访问方法:
使用宏来统一描述这个方法,来避免无谓的代码
/// Node_ heap data field access
macro_rules! def_node__heap_access {
(internal, $name:ident, $ret:ty) => {
fn $name(&self) -> &$ret {
match self {
Internal { $name, .. } => $name,
Leaf {..} => panic!(
"Get `{}` on leaf",
stringify!($name)
)
}
}
coll::paste!(
fn [<$name _mut>](&mut self) -> &mut $ret {
match self {
Internal { $name, .. } => $name,
Leaf {..} => panic!(
"Get `{}` on leaf",
stringify!($name)
)
}
}
);
};
(leaf, $name:ident, $ret:ty) => {
fn $name(&self) -> &$ret {
match self {
Internal {..} => panic!(
"Get `{}` on internal node",
stringify!($name)
),
Leaf { $name, ..} => $name
}
}
coll::paste!(
fn [<$name _mut>](&mut self) -> &mut $ret {
match self {
Internal {..} => panic!(
"Get `{}` on internal node",
stringify!($name)
),
Leaf { $name, ..} => $name
}
}
);
};
}
/// Node_ WeakNode field access
macro_rules! def_node__wn_access {
(both, $name:ident) => {
fn $name(&self) -> Node<K, V> {
match self {
Internal { $name, .. } => $name,
Leaf { $name, .. } => $name,
}
.upgrade()
}
coll::paste!(
fn [<set_ $name>](&mut self, x: Node<K, V>) {
match self {
Internal { $name, .. } => $name,
Leaf { $name, .. } => $name,
}
.replace(x.downgrade());
}
);
};
(leaf, $name:ident) => {
fn $name(&self) -> Node<K, V> {
match self {
Internal {..} => panic!(
"Get `{}` on internal node",
stringify!($name)
),
Leaf { $name, .. } => $name,
}
.upgrade()
}
coll::paste!(
fn [<set_ $name>](&mut self, x: Node<K, V>) {
match self {
Internal {..} => panic!(
"Get `{}` on internal node",
stringify!($name)
),
Leaf { $name, .. } => $name,
}
.replace(x.downgrade());
}
);
};
}
于是属性访问就可以写成:
impl<K, V> Node_<K, V> {
fn is_leaf(&self) -> bool {
matches!(self, Leaf { .. })
}
def_node__heap_access!(internal, keys, Vec<K>);
def_node__heap_access!(internal, children, Vec<Node<K, V>>);
def_node__heap_access!(leaf, entries, Vec<KVEntry<K, V>>);
def_node__wn_access!(both, paren);
def_node__wn_access!(leaf, succ);
def_node__wn_access!(leaf, pred);
}
这就可以写 B+ 树 专属的生成宏:
macro_rules! def_attr_macro_bpt {
($($name:ident),+) => {
$(
coll::paste!(
macro_rules! $name {
($node:expr) => {
attr!(self | $$node).$name()
};
($node:expr, $val:expr) => {
attr!(self_mut | $$node).[<set_ $name>]($$val)
};
}
);
coll::paste!(
#[allow(unused)]
macro_rules! [<$name _mut>] {
($node:expr) => {
attr!(self_mut | $$node).[<$name _mut>]()
};
}
);
)+
};
}
用它来生成节点包装 Node 的属性访问的宏:
def_attr_macro_bpt!(paren, pred, succ, keys, entries, children);
实现->基础方法
搜索到叶子节点
和 B 树的节点上的递归搜索方法一样,只是当在中间节点遇到相等的键时不是直接退出而是在它的右孩子上继续搜索。
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
#[inline(always)]
fn search_to_leaf<Q>(mut x: &Node<K, V>, k: &Q) -> Node<K, V>
where
K: Borrow<Q>,
Q: Ord + ?Sized,
{
while x.is_internal() {
match keys!(x).binary_search_by_key(&k, |k_| k_.borrow()) {
Ok(idx) => x = &children!(x)[idx + 1],
Err(idx) => {
x = &children!(x)[idx];
}
}
}
x.clone()
}
}
查询节点属性
impl<K, V> Node<K, V> {
fn is_leaf(&self) -> bool {
self.is_some() && attr!(self | self).is_leaf()
}
fn is_internal(&self) -> bool {
self.is_some() && !attr!(self | self).is_leaf()
}
pub fn max_key(&self) -> Option<&K> {
if self.is_none() {
None
}
else if self.is_internal() {
keys!(self).last()
}
else {
entries!(self).last().map(|ent| &ent.0)
}
}
pub fn min_key(&self) -> Option<&K> {
if self.is_none() {
None
}
else if self.is_internal() {
keys!(self).first()
}
else {
entries!(self).first().map(|ent| &ent.0)
}
}
}
最小/最大节点
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
#[inline(always)]
fn min_node(&self) -> Node<K, V> {
let mut x = &self.root;
while x.is_internal() {
x = &children!(x)[0];
}
x.clone()
}
#[inline]
fn max_node(&self) -> Node<K, V> {
let mut x = &self.root;
while x.is_internal() {
x = &children!(x).last().unwrap();
}
x.clone()
}
}
创建节点包装
macro_rules! node {
(kv| $k:expr, $v:expr) => { {
// overflow is M
let mut entries = Vec::with_capacity(M);
entries.push(KVEntry($k, $v));
node!(basic-leaf| entries, WeakNode::none(), WeakNode::none())
} };
(basic-leaf| $entries:expr, $succ:expr, $paren:expr) => { {
aux_node!(FREE-ENUM Leaf {
entries: $entries,
succ: $succ,
paren: $paren
})
} };
(basic-internal| $keys:expr, $children:expr, $paren:expr) => { {
aux_node!(FREE-ENUM Internal {
keys: $keys,
children: $children,
paren: $paren
})
} };
}
实现->简单方法
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
pub fn new() -> Self {
assert!(M > 2, "M should be greater than 2");
Self {
root: Node::none()
}
}
pub fn get<Q>(&self, k: &Q) -> Option<&V>
where
K: Borrow<Q>,
Q: Ord + ?Sized,
{
mut_self!(self).get_mut(k).map(|v| &*v)
}
pub fn get_mut<Q>(&mut self, k: &Q) -> Option<&mut V>
where
K: Borrow<Q>,
Q: Ord + ?Sized,
{
let x = Self::search_to_leaf(&self.root, k);
// Nil
if x.is_none() {
None
}
// Leaf
else {
debug_assert!(x.is_leaf());
match entries!(x).binary_search_by_key(&k, |ent| ent.0.borrow()) {
Ok(idx) => Some(&mut entries_mut!(x)[idx].1),
Err(_idx) => None,
}
}
}
}
实现->范围查询
使用前面二叉搜索树里的 mut_self 宏来少些一点儿代码
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
pub fn select<'a, Q, R: RangeBounds<&'a Q>>(
&self,
range: R,
) -> impl Iterator<Item = &V>
where
K: Borrow<Q>,
Q: Ord + ?Sized + 'a,
{
mut_self!(self).select_mut(range).map(|v| &*v)
}
pub fn select_mut<'a, Q, R: RangeBounds<&'a Q>>(
&mut self,
range: R,
) -> impl Iterator<Item = &mut V>
where
K: Borrow<Q>,
Q: Ord + ?Sized + 'a,
{
/* find start_node */
let mut cur;
let mut idx = 0;
match range.start_bound() {
Included(&k) => {
let x = Self::search_to_leaf(&self.root, k.borrow());
// Nil
if x.is_none() {
cur = Node::none();
}
// Leaf
else {
match entries!(x)
.binary_search_by_key(&k, |ent| ent.0.borrow())
{
Ok(idx_) => idx = idx_,
Err(idx_) => idx = idx_,
};
cur = x;
}
}
Excluded(_) => unimplemented!(),
Unbounded => {
cur = self.min_node();
}
}
if cur.is_some() && idx == entries!(cur).len() {
cur = succ!(cur);
idx = 0;
}
std::iter::from_generator(move || {
if cur.is_none() {
return;
}
let mut entries = &mut entries_mut!(cur)[idx..];
loop {
for ent in entries {
if range.contains(&ent.0.borrow()) {
yield &mut ent.1
} else {
return;
}
}
cur = succ!(cur);
if cur.is_none() {
break;
}
entries = &mut entries_mut!(cur)[..];
}
})
}
}
实现->插入
插入主流程
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
pub fn insert(&mut self, k: K, v: V) -> Option<V>
where
K: Clone,
{
let x = Self::search_to_leaf(&self.root, &k);
self.insert_into_leaf(x, k, v)
}
fn insert_into_leaf(&mut self, x: Node<K, V>, k: K, v: V) -> Option<V>
where
K: Clone,
{
/* NonInternal Node */
debug_assert!(!x.is_internal());
/* Nil */
if x.is_none() {
self.root = node!(kv | k, v);
}
/* Leaf */
else {
let idx = match entries!(x).binary_search_by_key(&&k, |ent| &ent.0)
{
Ok(idx) => {
return Some(replace(&mut entries_mut!(x)[idx].1, v))
}
Err(idx) => idx,
};
/* insert into leaf */
entries_mut!(x).insert(idx, KVEntry(k, v));
self.insert_retracing(x);
}
self.cnt += 1;
None
}
}
节点提升方法
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
fn insert_retracing(&mut self, x: Node<K, V>)
where
K: Clone,
{
if entries!(x).len() == M {
self.promote(x);
}
}
fn promote(&mut self, x: Node<K, V>)
where
K: Clone,
{
debug_assert!(x.is_some());
let p = paren!(x);
/* split node */
let lpos = M.div_floor(2);
let hpos = M.div_ceil(2);
let head_key;
let x2;
if x.is_leaf() {
debug_assert_eq!(entries!(x).len(), Self::entries_high_bound());
// keep key for leaf
let entries_x2 = entries_mut!(x).split_off(lpos);
head_key = entries_x2[0].0.clone();
x2 = node!(
basic - leaf | entries_x2,
succ!(x).downgrade(),
WeakNode::none()
);
succ!(x, x2.clone());
} else {
debug_assert_eq!(keys!(x).len(), Self::entries_high_bound());
let keys_x2 = keys_mut!(x).split_off(hpos);
head_key = keys_mut!(x).pop().unwrap();
let children_x2 = children_mut!(x).split_off(hpos);
x2 = node!(
basic - internal | keys_x2,
children_x2,
WeakNode::none()
);
children_revref!(&x2);
}
/* push new level */
if p.is_none() {
let keys = vec![head_key];
let children = vec![x, x2];
self.root =
node!(basic - internal | keys, children, WeakNode::none());
children_revref!(&self.root);
}
/* insert into paren node */
else {
let x_idx = index_of_child!(p, &x);
keys_mut!(p).insert(x_idx, head_key);
children_mut!(p).insert(x_idx + 1, x2.clone());
paren!(x2, p.clone());
if keys!(p).len() == Self::entries_high_bound() {
self.promote(p);
}
}
}
}
实现->删除
这里特别需要注意的是,
删除主流程
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
pub fn remove<Q>(&mut self, k: &Q) -> Option<V>
where
K: Borrow<Q> + Clone,
Q: Ord + ?Sized,
V: Debug,
{
let mut x = &self.root;
let mut internal_and_idx = None;
while x.is_internal() {
match keys!(x).binary_search_by_key(&k, |k_| k_.borrow()) {
Ok(idx) => {
debug_assert!(internal_and_idx.is_none());
internal_and_idx = Some((x.clone(), idx));
x = &children!(x)[idx + 1];
}
Err(idx) => {
x = &children!(x)[idx];
}
}
}
if x.is_none() {
return None;
}
let idx;
match entries!(x).binary_search_by_key(&k, |ent| ent.0.borrow()) {
Ok(idx_) => idx = idx_,
Err(_idx) => return None,
}
self.remove_on_leaf(internal_and_idx, x.clone(), idx)
.map(|(_, v)| v)
}
fn remove_on_leaf(
&mut self,
internal_and_idx: Option<(Node<K, V>, usize)>,
x: Node<K, V>,
idx: usize,
) -> Option<(K, V)>
where
K: Clone,
{
/* Update internal key with its succsessor key */
if let Some((internal, i_idx)) = internal_and_idx {
self.update_internal_key(&internal, i_idx, &x, idx);
}
let popped = entries_mut!(x).remove(idx);
self.remove_retracing(x.clone());
Some((popped.0, popped.1))
}
}
更新索引
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
fn update_internal_key(
&self,
internal: &Node<K, V>,
i_idx: usize,
x: &Node<K, V>,
idx: usize,
) where
K: Clone,
{
debug_assert!(x.is_leaf());
let p = paren!(x);
debug_assert!(p.is_some());
let new_key;
if entries!(x).len() > 1 {
// left first
if idx > 0 {
new_key = entries!(x)[idx - 1].0.clone();
} else {
new_key = entries!(x)[idx + 1].0.clone();
}
} else {
let x_idx = index_of_child!(p, x);
/* check remain node */
// left first
if x_idx > 0 && entries!(children!(p)[x_idx - 1]).len() > 1 {
new_key = children!(p)[x_idx - 1].max_key().unwrap().clone();
}
// right sib
else if x_idx < children!(p).len() - 1
&& entries!(children!(p)[x_idx + 1]).len() > 1
{
new_key = entries!(succ!(x))[0].0.clone();
}
/* use default (left first)*/
else if x_idx > 0 {
new_key = children!(p)[x_idx - 1].max_key().unwrap().clone();
} else {
new_key = entries!(succ!(x))[0].0.clone();
}
}
keys_mut!(internal)[i_idx] = new_key;
}
}
节点下降
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
fn unpromote(&mut self, mut x: Node<K, V>)
where
K: Clone,
{
// Exclude leaf node and nil node
debug_assert!(x.is_some());
debug_assert!(
x.is_leaf() || keys!(x).len() == Self::entries_low_bound() - 1
);
if let Err((p, idx)) = self.try_rebalancing(&x) {
if idx == 0 {
merge_node!(p, idx);
} else {
merge_node!(p, idx - 1);
}
x = p;
if paren!(x).is_none() {
// pop new level
if keys!(x).is_empty() {
self.root = children_mut!(x).pop().unwrap();
paren!(self.root, Node::none());
}
} else {
if keys!(x).len() < Self::entries_low_bound() {
self.unpromote(x);
}
}
}
}
}
尝试重平衡
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
fn try_rebalancing(&mut self, x: &Node<K, V>)
-> std::result::Result<(), (Node<K, V>, usize)>
where
K: Clone,
{
debug_assert!(paren!(x).is_some());
/* Check if siblings has remains */
let p = paren!(x);
let idx = index_of_child_by_rc!(p, x);
// Left first
if idx > 0 {
try_node_redistribution!(p, idx - 1, Left);
}
if idx < children!(p).len() - 1 {
try_node_redistribution!(p, idx, Right);
}
Err((p, idx))
}
}
macro_rules! try_node_redistribution {
($p:expr, $idx:expr, $sib_dir:expr) => { {
let p = &$p;
let idx = $idx;
let sib_dir = $sib_dir;
let children = children!(p);
let left = &children[idx];
let right = &children[idx + 1];
let sib = if sib_dir.is_left() { left } else { right };
if sib.is_leaf() && entries!(sib).len() > 1 {
if sib_dir.is_left() {
entries_mut!(right).insert(
0,
entries_mut!(left).pop().unwrap()
);
}
// sib is right
else {
entries_mut!(left).push(
entries_mut!(right).remove(0)
);
keys_mut!(p)[idx] = entries!(right)[0].0.clone();
}
return Ok(());
}
if sib.is_internal() && keys!(sib).len() > Self::entries_low_bound() {
if sib_dir.is_left() {
keys_mut!(right).insert(
0,
replace(
&mut keys_mut!(p)[idx],
keys_mut!(left).pop().unwrap(),
),
);
let child = children_mut!(left).pop().unwrap();
paren!(child, right.clone());
children_mut!(right).insert(0, child);
} else {
keys_mut!(left).push(replace(
&mut keys_mut!(p)[idx],
keys_mut!(right).remove(0),
));
let child = children_mut!(right).remove(0);
paren!(child, left.clone());
children_mut!(left).push(child);
}
return Ok(());
}
} };
}
合并节点
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
/// (parent, left-idx)
fn merge_node(&mut self, p: &Node<K, V>, idx: usize) {
let children = children!(p);
let left = children[idx].clone();
let right = children[idx + 1].clone();
// for leaf node
if left.is_leaf() {
keys_mut!(p).remove(idx);
entries_mut!(left).extend(entries_mut!(right).drain(..));
// update succ
succ!(left, succ!(right));
// update pred
if succ!(right).is_some() {
pred!(succ!(right), left.clone());
}
// update max_node
if right.rc_eq(&self.max_node.upgrade()) {
// update max_node
self.max_node = left.downgrade();
}
}
// for internal node
else {
keys_mut!(left).push(keys_mut!(p).remove(idx));
keys_mut!(left).extend(keys_mut!(right).drain(..));
// merge right's children to the left
let left_children = children_mut!(left);
for child in children_mut!(right).drain(..) {
paren!(child, left.clone());
left_children.push(child);
}
}
// remove right from p
children_mut!(p).remove(idx + 1);
}
}
实现->测试
打印方法
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
fn debug_write<W: std::fmt::Write>(&self, f: &mut W) -> std::fmt::Result
where
V: Debug,
{
/* print header */
writeln!(f, "{self:?}")?;
/* print body */
if self.root.is_none() {
return Ok(());
}
let mut this_q = crate::vecdeq![vec![self.root.clone()]];
let mut lv = 1;
while !this_q.is_empty() {
writeln!(f)?;
writeln!(f, "############ Level: {lv} #############")?;
writeln!(f)?;
let mut nxt_q = crate::vecdeq![];
while let Some(children) = this_q.pop_front() {
for (i, x) in children.iter().enumerate() {
let p = paren!(x);
if x.is_internal() {
nxt_q.push_back(children!(x).clone());
writeln!(f, "({i:02}): {x:?} (p: [{p:?}])")?;
} else {
let succ = succ!(x);
writeln!(
f,
"({i:02}): {x:?} (p: [{p:?}], succ: [{succ:?}])"
)?;
}
}
writeln!(f)?;
}
this_q = nxt_q;
lv += 1;
}
writeln!(f, "------------- end --------------\n")?;
Ok(())
}
fn debug_print(&self)
where
V: Debug,
{
let mut cache = String::new();
self.debug_write(&mut cache).unwrap();
println!("{cache}")
}
}
性质校验
impl<K: Ord, V, const M: usize> BPT<K, V, M> {
fn validate(&self)
where
K: Debug,
{
if self.root.is_none() {
return;
}
use std::collections::VecDeque;
use crate::vecdeq;
let mut cur_q = vecdeq![vecdeq![Node::none(), self.root.clone()]];
while !cur_q.is_empty() {
let mut nxt_q = vecdeq![];
let mut leaf_num = 0;
let mut internal_num = 0;
while let Some(mut group) = cur_q.pop_front() {
let p = group.pop_front().unwrap();
for child in group.iter() {
assert!(child.is_some());
if child.is_internal() {
assert_eq!(
keys!(child).len() + 1,
children!(child).len(),
"{child:?}"
);
assert!(
children!(child).len() <= M,
"{child:?}: {}",
children!(child).len()
);
assert!(
keys!(child).len() < Self::entries_high_bound()
);
} else {
assert!(
entries!(child).len() < Self::entries_high_bound()
);
}
// Exclude leaf
if child.is_leaf() {
if p.is_some() {
let idx = index_of_child!(p, child);
if idx > 0 {
assert_eq!(
keys!(p)[idx - 1],
entries!(child)[0].0
);
}
}
leaf_num += 1;
} else {
// Exclude the root (which is always one when it's internal node)
if paren!(child).is_some() {
assert!(
keys!(child).len()
>= Self::entries_low_bound()
);
} else {
assert!(children!(child).len() >= 2);
}
/* search obsoleted key */
for k in keys!(child) {
let leaf = search_to_leaf!(child, k);
if leaf.is_none()
|| entries!(leaf).binary_search_by_key(
&k, |ent| &ent.0
).is_err()
{
panic!("Found obsoleted key: {k:?}");
}
}
internal_num += 1;
let mut nxt_children =
VecDeque::from(children!(child).clone());
nxt_children.push_front(child.clone());
nxt_q.push_back(nxt_children);
}
}
// All leaves are in same level
assert!(
leaf_num == 0 || internal_num == 0,
"leaf: {leaf_num}, internal: {internal_num}"
);
// Ordered
if p.is_some() {
let last_child = group.pop_back().unwrap();
for (i, child) in group.iter().enumerate() {
if child.is_leaf() {
assert!(entries!(child).is_sorted());
} else {
assert!(keys!(child).is_sorted());
}
let child_max_key = last_key!(child);
let branch_key = key!(&p, i);
assert!(
child_max_key < branch_key,
"child: {child_max_key:?}, branch:{branch_key:?}"
);
if i > 0 {
assert!(key!(&p, i - 1) <= key!(child, 0));
}
}
assert!(last_key!(&p) <= key!(&last_child, 0));
}
}
cur_q = nxt_q;
}
}
}
总结
- 2024-12-05 推荐使用 M=32
